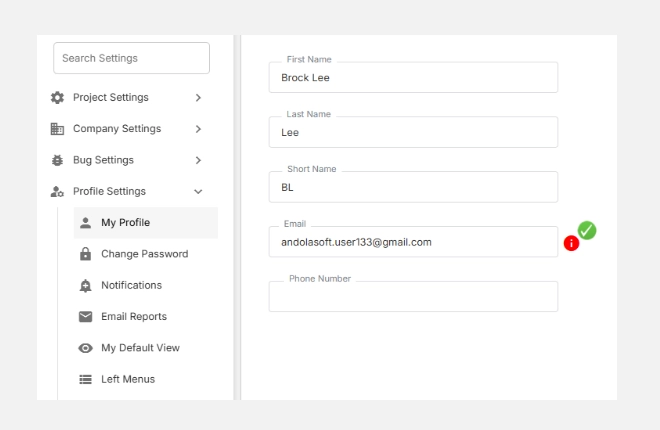
The My Profile section allows each user to personalize their Orangescrum experience by managing their identity, contact details, and workspace preferences.
Here, you can update your name, email, time zone, language, time format, and upload a profile image — ensuring your account is accurate and consistent across your projects.
Keeping your profile updated helps team members identify you easily in projects, tasks, and reports.
Fields Available in My Profile
| Field | Description |
| First Name / Last Name | Your official name as it appears across projects, tasks, and communications. |
| Short Name | Abbreviation or initials (e.g., AN) used in dashboards, comments, and quick views. |
| Your registered email address used for login and notifications. | |
| Phone Number | Optional — add your contact number for internal reference or team directories. |
| Time Zone | Choose your preferred time zone to ensure all tasks, logs, and reports show accurate timestamps. |
| Daylight Saving (DST) | Enable or disable DST adjustments based on your region. |
| Language | Select your preferred language for interface labels and menus. |
| Time Format | Choose between a 12-hour or 24-hour format for all date/time displays. |
| Skills | Mention your core skills or areas of expertise — useful for team visibility and resource allocation. |
| Profile Image | Upload a profile photo to personalize your workspace and make collaboration more intuitive. |
How to Update Your Profile
- Go to Settings → Profile Settings → My Profile.
- Update the desired fields such as name, email, or timezone.
- Click Save to apply your changes.
- Your updates will instantly reflect across your Orangescrum account.
Best Practices
✅ Use your official name and company email for team identification.
✅ Keep your time zone and language settings aligned with your working location.
✅ Update your profile photo to help teammates recognize you in discussions and reports.
✅ Review and refresh your details periodically, especially when changing roles or locations.
With My Profile in Orangescrum Cloud, every user can create a personalized workspace that reflects their identity, time preferences, and communication style — ensuring smoother collaboration and better visibility across teams.